What are 16 Major Losses in TPM?
→ Losses in the production process mean the top most quantities of material, money, energy, and time are wasted.
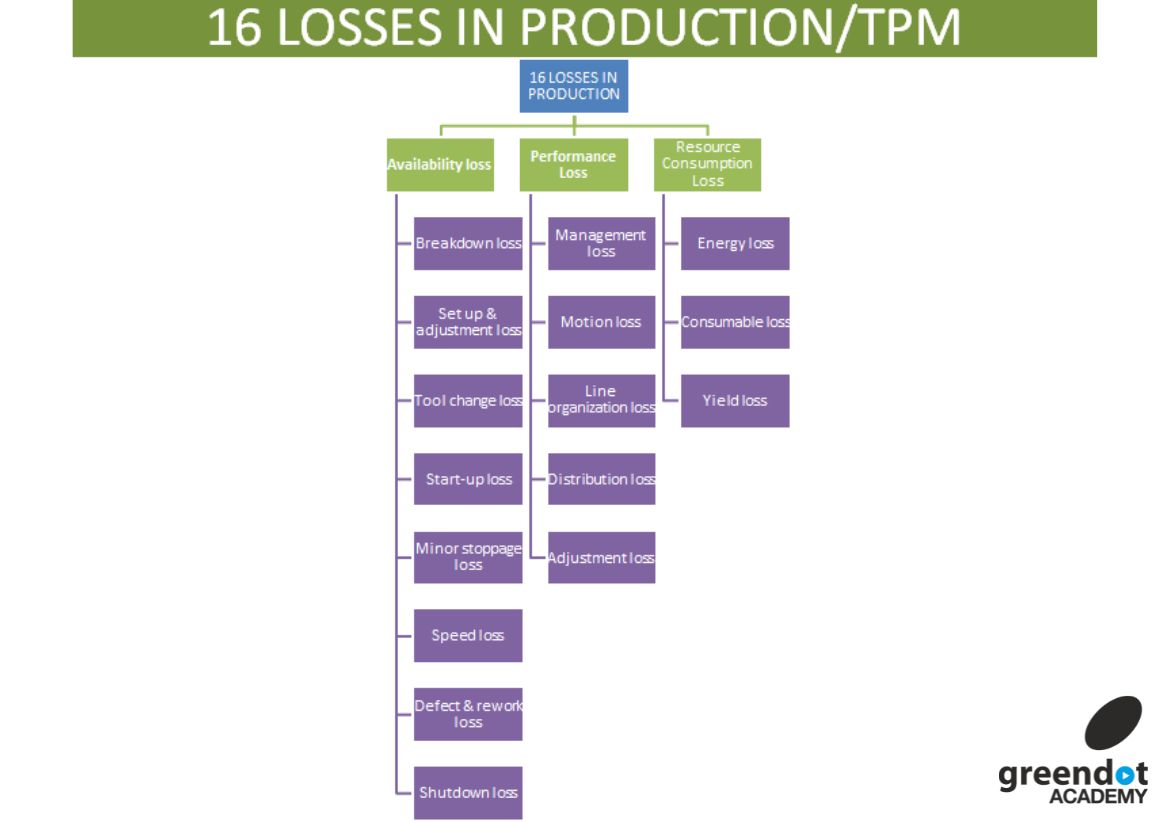
→ In Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), there are 16 defined set of criteria related to several losses, which is known as 16 Major Losses.
→ The names of these losses might be different in different associations, but the orders and concept are the same.
→ These 16 Major Losses in Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) impact on Product Quality,productivity, and profitability of the association.
→ So we need to identify and erase these losses from the association.
→ Some of the reasons for the losses can be summarized as below
⇢ We're running production for extra timing.
⇢ Production is interrupt or stopped
⇢ Non- value- adding activity is performed
⇢ The machine is idle or we can say not planning
⇢ When a machine isn't running as per the design rated
speed
⇢ The machine is consuming extra time, money, energy than the specified demand.
The 16 Major Losses in Production
→ The 16 Major losses in Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) are further divided into different orders as mentioned below
1. Losses Impacting on Availability-8 Losses ( Relate 1 to 8 Losses in the below list)
2. Losses Impacting on Performance-5 Losses ( Relate 9 to 13 Losses in the below list)
3. Losses Impacting on Resource Consumption-3 Losses ( Relate 14 to 16 Losses in the below list)
→ For better understanding, You can relate to Overall Outfit Effectiveness (OEE).

The 16 Major losses in TPM are given below
1. Equipment Failure ( Breakdown) Loss
2. Set up & Adjustment Loss
3. Cutting Tool/ Blade Change Loss
4. Start-up Loss
5. Minor Stoppage & Idling Loss
6. Speed Loss
7. Defect & Rework Loss
8. Shutdown Loss (Planned Maintenance Loss)
9. Management Loss
10. Motion Loss or Operating Motion Loss
11. Line Organization Loss
12. Distribution/ Logistic Loss
13. Measurement & Adjustment Loss
14. Energy Loss
15. Consumable Loss
16. Yield Loss
8 Types of Losses- Impacting on availability
01. Equipment Failure ( Breakdown) Loss
→ Equipment Failure means the machine is under any kind of breakdown and not suitable to operate.
→ We can also include the failure-if the machine isn't suitable to operate at rated capacity due to a technical problem.
→ Our target is zero breakdowns.
→ For this kind of failure generally, we're doing Breakdown
→ We can remove Equipment failure by implementing a Preventive Maintenance Plan.
02. Set up & Adjustment Loss
→ While we've any transformation on the machine at that time we've a loss that's called setup and adjustment loss.
→ The transformation includes product transformation, jig/ fixture transformation, tool/ die transformation,etc.
→ We can use the Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) technique for minimizing
Setup & Adjustment Loss.
03. Cutting Tool/ Blade change Loss
→ While we're changing or replacing the cutting tool/ blade at that time the loss is created that's known as a Cutting Tool/ Blade change loss.
→ We're changing several tools like a drill bit, grinding wheel, tap, rammer, cutter,etc.
→ We can use the Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) fashion for minimizing
Setup & Adjustment Loss.
→ Also, alternately, we can develop a more durable cutting tool or implement several
.Kaizens for reducing this loss.
04. Start-up Loss
→ A Start-up loss occurs while we're starting the machine.
→ It includes stabilize the production and need to take approval from QA before continuing the production.
→ So this loss considers as a startup loss until the machine runs at rated speed.
→ As per the manufacturing product, the startup process may include the production
. process, cleaning, conditioning, → We can reduce this loss by standardizing the processes and parameters.
05. Minor Stoppage & Idling Loss
→ While machine stops constantly for a very small time period and this activity occurs multiple times in a shift that's considered the minor stoppages and Idling Loss.
→ Minor stoppages might be possible due to malfunction of detectors, jamming of product, resetting parameters,etc.
→ Sometimes we stop machines for a job removing or resetting that's also an illustration of Minor Stoppage.
06. Speed Loss
→ If the machine is running lower than the design speed also it's considered as the speed loss.
→ If the machine's rated design speed is 60 products per nanosecond and we're getting the actual output is products per min also there's a speed loss of 5 products per min.
→ So our target should be the machine must be running at the design speed for minimizing the speed loss.
07. Defect & Rework Loss
→ If the machine is producing a defective product and we're spending time to rework the defective product that's called the Defect and Rework Loss.
→ For removing this loss we need to Standardize processes and parameters.
→ For better understanding, you can relate to the 5S Methodology.
08. Shut down Loss (Planned Maintenance Loss)
→ When Equipment is shut down for the Planned maintenance, the loss is considered a shutdown Loss or Planned Maintenance Loss.
→ Sometimes the equipment should be shut down due to periodic examination, statutory or regulartory compliance.
5 Types of Losses- Impacting on Performance
09. Management Loss
→ The Waiting losses that are caused by management are called Management Loss.
→ Some example of management losses are waiting for materials, waiting for machine reserves, waiting for tools, waiting for instructions, waiting for man force,etc.
10. Motion Loss or Operating motion Loss
→ If we take extra motion/step for any process so that's known as a motion
Loss or Operating motion Loss.
→ This happens mainly due to efficiency process layout.
→ To minimize or remove this loss we need to implement automation or optimize the process layout and step.
11. Line Organization Loss
→ Line balancing loss is the waiting loss at the process level.
→ Line balancing means if any product is manufactured in four way also the speed of all way or all stations should be the same.
→ The product shouldn't be ideal at any stage of the process.
→ To remove this loss we need to use the Line Balancing or Bottleneck Analysis Concept.
12. Distribution Loss
→ Distribution Loss is related to man-hour losses due to transport of material, semi finished products, or finished products from one place to another.
→ To remove this kind of loss we can implement automation for material/ product transportation at different level.
13. Measurement & Adjustment Loss
→ The man-hour loss is due to frequent measurement & adaptation of machine settings to prevent the quality defect is called a Measurement & Adjustment Loss.
→ That's happening during continuous production.
→ So we can minimize this kind of loss by implement several Poka Yoke and Process Standardization.
3 Types of Losses- Impacting on Resources Consumption
14. Energy Loss
→ The losses due to ineffective utilization of input energy like electric, gas, fuel , oil, steam, air, and water, etc in processing is called Energy Loss.
→ Examples of Energy Loss are losses due to heat radiation, leakage of fuel, leakage of air, Leakage of oil,etc.
→ Energy loss has a high impact on total cost so we need to minimize this kind of loss
15. Consumable Loss
→ The losses due to repair and replacement of any spare, die, tool, etc is called Consumable loss.
→ Extra get damaged after the service life so we need to change it-this is coming under the consumable loss.
16. Yield Loss
→ Sometimes the weight of the finished product is advanced than the design specification that's due to maintaining the good quality of the product but it's a loss of the is called Yield Loss.
→ Sometimes rather of excess material, excess processing is needed for a good quality product that's also a Yield Loss.
→ For better understanding we take one illustration- Increase casting wall width to avoid blow- holes defect leading to more machining time and loss of material.